This article will demonstrate the forensic backup feature of Acronis Cyber Protect. A forensic backup is a bit by bit, sector by sector direct copy of a physical storage device. This includes all files, folders, and unallocated free space as well as slack space. Slack space is the leftover storage that exists on a computer's hard disk drive when a computer file does not need all the space it has been allocated by the operating system. A forensic backup also includes a memory dump and a snapshot of running processes. There are a number of reasons for having a forensic backup including:
- Log monitoring to analyze log entries and correlate log entries across many systems to help assist in identifying policy violations, auditing, and incident handling.
- Data recovery for retrieving data that has been accidentally or purposefully deleted or modified.
- Due diligence in regulatory compliance. Existing or emerging regulations might require companies to protect sensitive information and maintain certain records for audit purposes. In the event protected information gets exposed to other parties, a company may be required to notify other agencies or individuals that have been impacted. A forensic backup can assist companies to exercise due diligence and comply with such requirements.
To create a forensic backup in a protection plan within the Acronis Cyber Protect, follow the procedure below.
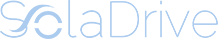
Step 1: Navigate to "Plans" on the left-hand side menu, then go to "Protection". On the right-hand side menu, click on "Create plan". It is recommended to create a separate plan only for forensic backup. You should therefore disable all other modules except for "Backup" as shown below.
Step 2: Make sure that "Entire machine" is selected under "What to backup" as shown above.
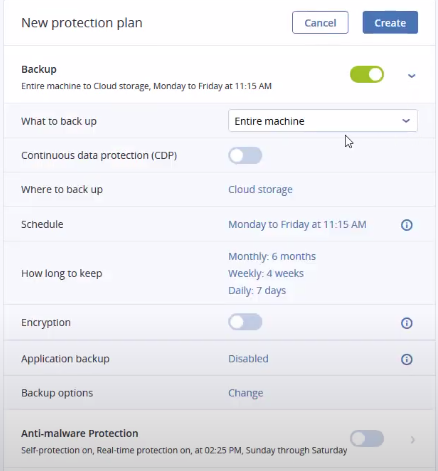
Step 3: Under "Backup options", click on "Change" and navigate down to "Forensic options". You will see the screen below. Enable the "Collect forensic data" toggle as shown.
Step 4: You have the option to select a device at this time or you can add a device to the plan later when you want to perform a forensic backup. Additionally, you can schedule these backups or have them not scheduled to perform the forensic backup on demand. Click on the "Create" button.
Acronis Cyber Protect will perform the following functions during the forensic backup process:
- Collect a raw memory dump and a list of running processes. It is important to note that a full memory dump may contain sensitive data such as passwords.
- Automatically reboot the machine into bootable media.
- Create a backup that includes both the occupied and unallocated space.
- Notarize the backup.
- Reboot into the live OS and continue the protection plan execution e.g. any replication, retention, validation, or other functions defined in the protection plan.
It is important to note that once the protection plan is applied, the forensic data settings cannot be modified. To change something, you will need to create a whole new protection plan with the desired settings. Supported locations for backups with forensic data can be either cloud storage or a local folder. However, the local folder is only supported on an external hard drive connected via USB. Local dynamic disks are not supported as a location for forensic backups. Network folders are allowed as well.
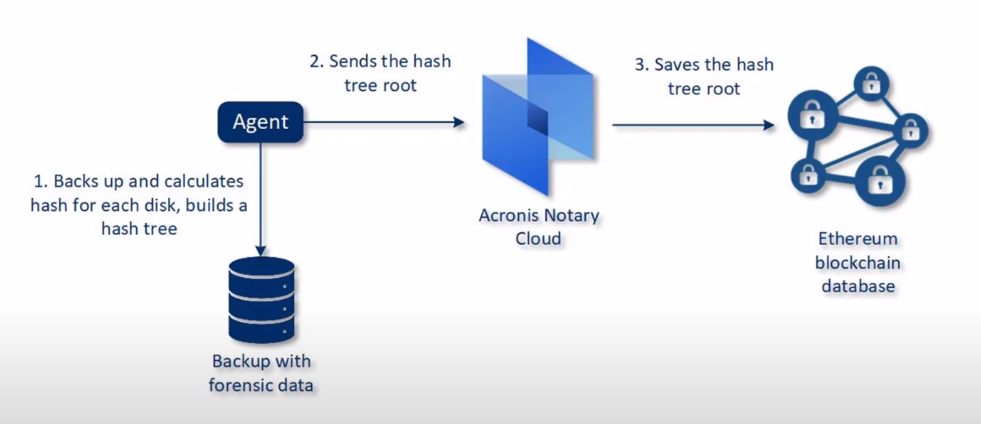
When you back up with forensic data, this backup is automatically notarized. This ensures the data that is backed up forensically is exactly the image taken and was not compromised for proper chain of custody. During the forensic backup, the agent calculates the hash code for each disk, builds a hash tree, saves the tree in the backup, and sends the hash tree root to the notary service. The notary service will save the hash tree root in an Etherium blockchain database to make sure the value does not change. To verify authenticity, the agent calculates the hash of the disk and compares it to the hash stored in the hash tree inside the backup. Further, to ensure the hash tree was not compromised, the agent sends the hash tree root to the notary service. Then the service compares it to the one stored in the blockchain database. If the hashes match, then it is authentic. If not, then the software will display a message that says the disk is not authentic. See illustration below.
How often to create a forensic backup depends on the company and any regulatory compliance one might fall under. Acronis Cyber Protect provides the flexibility in protection plans to address this.